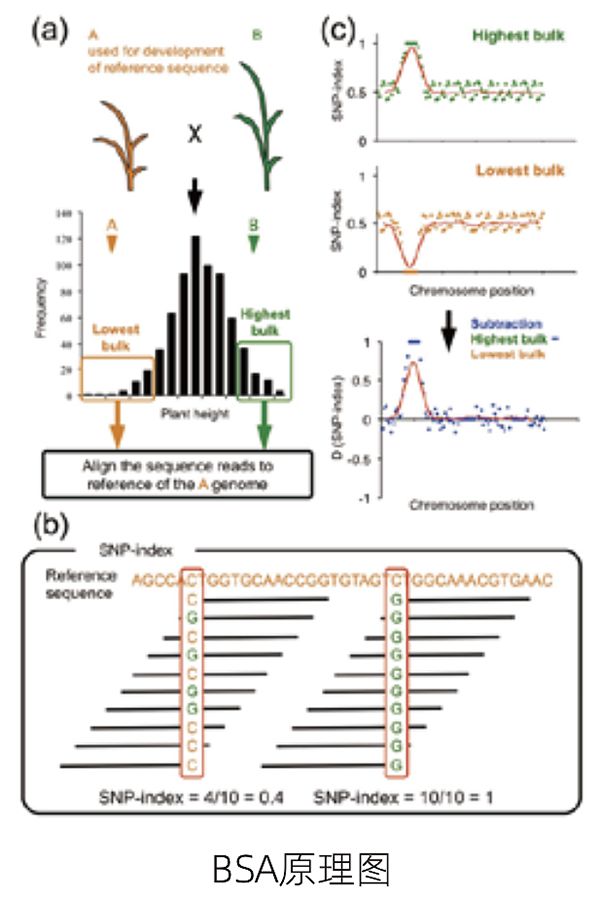
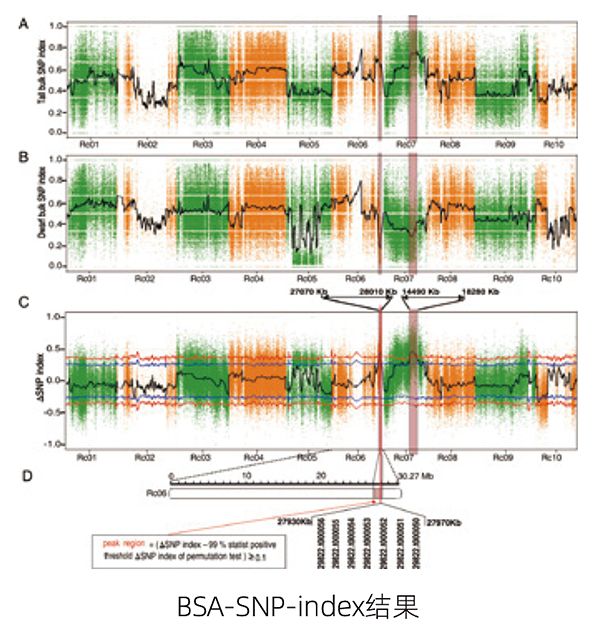
Bulked segregant analysis(BSA)
Whole Genome Resequencing
By sequencing the genomes of different individuals or groups of species with reference genome sequences and analyzing the genome differences of individuals or groups, we can quickly evaluate and screen resources, obtain a large number of genetic variation, and realize genetic population structure, evolutionary analysis, location of important candidate genes, screening and development of functional gene molecular markers. Whole genome resequencing is an effective method for animal and plant breeding and population evolution.
BSA (bulked segregant analysis), that is, separated population grouping analysis or mixed grouping analysis, is a method to detect the loci associated with specific target traits on specific chromosome segments. Individuals with extreme or representative traits were selected from the population to form a mixed pool. By studying the difference of allele / molecular marker frequency between the mixed pools, the loci related to the traits were quickly located in the genome.
The application of high-throughput genotyping technologies such as whole genome resequencing, precise location sequencing typing (MGPS, cgps) and chip has significantly improved the efficiency of quantitative trait locus mapping using BSA method.